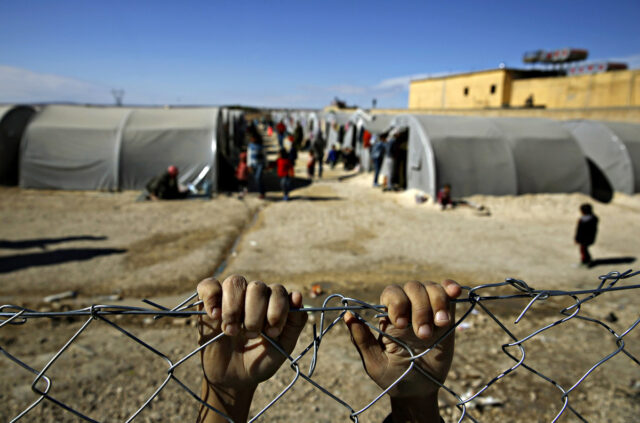
Assessing Immigration Impacts in Developing Countries. The Case of Syrian Refugees in Lebanon
By Riccardo Magnani & Marie-Claude KAMAR This article analyzes the effects of low-skilled immigration in developing countries characterized by a large informal sector, high unemployment (especially among highly educated people), and low participation of women in the labor force. We use an OLG model to account for the general equilibrium linkages between the immigration shock, the level of wages and employment, the education choice, and the emigration choice made by natives. The model includes search and matching frictions in the...